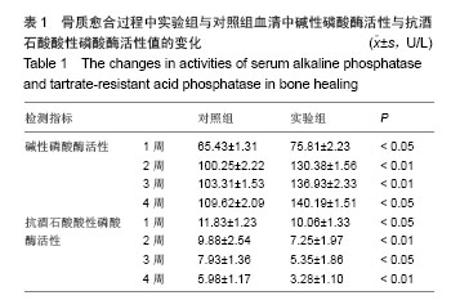
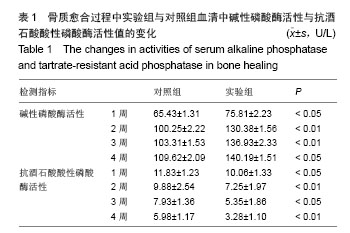
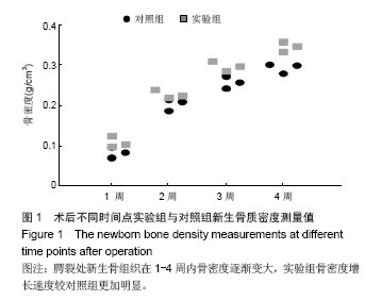
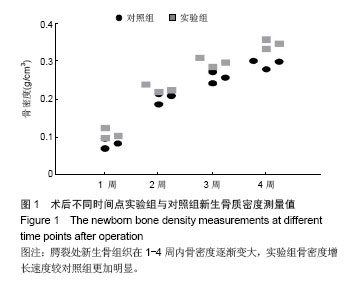
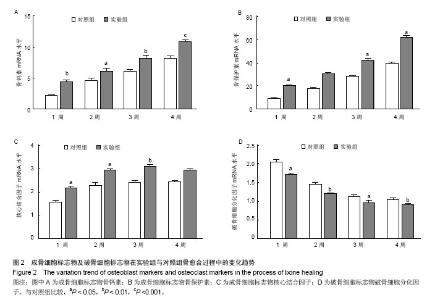
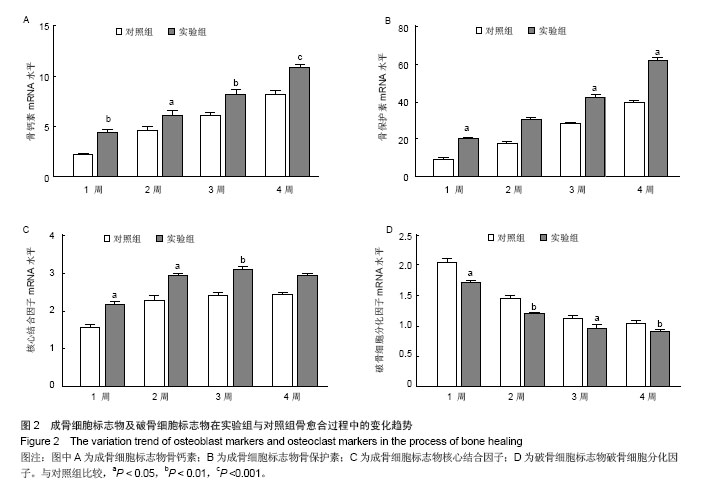
| [1]Gritli-Linde A.Molecular control of secondary palate development.Dev Biol.2007;301(2):309-326.
[2]Philips BJ.Parameters for Evaluation and Treatment of Patients with Cleft Lip/Palate or the Craniofacial Anomalies. American cleft palate-cranofacial association, 1993:14.
[3]Bergland O,Semb G,Abyholm F.Elimination of the residual alveolar clefts by secondary bone grafting and subsequent orthodontic treatment. Cleft Palate J. 1986;23:175-205.
[4]陈仁吉.唇腭裂患者牙槽突裂骨缺损修复材料的现状及发展方向[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2012,5(6):340-345.
[5]庄飚,马莲.骨形成蛋白在不同年龄唇腭裂患者髂骨中的表达[J].北京口腔医学, 2007,15(6):316-318.
[6]Rawashdeh MA,Telfah H.Secondary alveolar bone grafting: the dilemma of donor site selection and morbidity.Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2008;46(8):665-670.
[7]De Riu G,Meloni SM,Raho MT,et al.Delayed iliac abscess as an unusual complication of an iliac bone graft in an orthognathic case.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2008; 37(12): 1156-1158.
[8]Bajaj AK,Wongworawat AA,Punjabi A.Management of alveolar clefts. J Craniofac Surg.2003;14(6):840-846.
[9]王刚,张文云.人工骨修复牙槽骨缺损的研究进展[J].西南国防医学,2014,24(4):455-456.
[10]Fu YC,Nie H,Ho ML,et al.Optimized bone regeneration based on sustained release from three-dimensional fibrous PLGA/ Hap composite scaffolds loaded with BMP-2.Biotechnol Bioeng.2008;99(4):996-1006.
[11]曲志强,何慕舜,曾月东,等.骨形态发生蛋白与骨缺损的修复[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(2):345-348.
[12]Bonner M,Ward IM,McGregor W,et al. Hydroxyapatite/ polypropylene composite:a novel bone substitute material.J Mater Sci Lett.2001;20(22):2049-2051.
[13]Itoh S,Kikuchi M,Takakuda K.The biocompatibility and osteoconductive activity of a novel hydroxyapatite/collagen composite biomaterial,and its function as a carrier of rhBMP-2.J Biomed Mater Res.2001;54(3):445-453.
[14]Hu Q,Li B,Wang M,et al.Preparation and characterization of biodegradable chitosan/hydroxyapatite nanocomposite rods via in situ hybridization: a potential material as internal fixation of bone fracture.Biomaterials. 2004;25(5):779-785.
[15]Pan Y,Xiong D,Gao F.Viscoelastic behavior of nano-hydroxyapatite reinforced poly(vinyl alcohol) gel biocomposites as an articular cartilage.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2008;19(5):1963-1969.
[16]王学江,李玉宝.羟基磷灰石纳米针晶与聚酰胺仿生复合材料研究[J].高科技通讯,2001,11(5):1-5.
[17]李毅,孟国林,刘建,等.MPC骨水泥纤维蛋白胶复合BMP人工骨支架材料对山羊松质骨缺损的修复[J].科学技术与工程, 2008, 8(6):1414-1418.
[18]陈鹏,刘冰.活性纳米羟基磷灰石复合胶原/聚乳酸材料修复颅骨极限缺损的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2007,21(11): 1191-1195.
[19]刘鹏.纳米羟基磷灰石-胶原-重组人骨形成蛋白-2复合支架的制备及细胞相容性[D].山西医科大学,2012:1-35.
[20]Siegel MI,Mooney MP.Appropriate animal models for caniofacial biology. Cleft Palate J.1990;27(1):18-25.
[21]Bardach J,Kelly KM.Does interference with mucoperiosteum and palatal bone affect maxillofacial surgery? Plast Reconstr Surg.1991;88(3):545-548.
[22]Wang YJ,Tong YQ,Dai Q,et al.The influence of autogenous bone graft in cleft palate on maxillary growth: an experiment study in rats.Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue.2005;14(1):37-41.
[23]Kudoh A.Effects of hyperbaric oxygen treatment on healing of maxillary distraction osteogenesis in beagle dogs. Kokubyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2008;75(1):55-64.
[24]Djasim UM,Hekking-Weijma JM,Wolvius EB,et al.Rabbits as a model for research into craniofacial distraction osteogenesis.Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;46(8):620-624.
[25]黄洪章,傅豫川,刘恭奇,等.腭成形术对人工腭裂大鼠上颌牙列发育影响的研究[J].口腔医学纵横杂志,1995,11(3):139-140.
[26]Schmitz JP,Hollinger JO.The critical size defect as an experimental model for craniomandibulofacial nonunions.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1986;205:299-308.
[27]佘小明,金鑫,田锟,等.植入成品骨诱导活性材料修复腭裂骨缺损:随机对照3个月后腭部CT扫描三维重建[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(42):8225-8228.
[28]Urist MR.Bone: formation by autoinduction. Science. 1965; 150(698):893-899.
[29]赵星,王愉思,何畔.骨形态发生蛋白最新研究及应用[J].医学信息,2014,28(3):538.
[30]石冰.唇腭裂修复外科学[M].成都:四川大学出版社,2004:388- 405.
[31]Boyarskiy S,Choi HJ,Park K.Evaluation of alveolar bone support of the permanent canine in cleft and noncIeft patients. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2006;43(6):678-682.
[32]李希.双能量X线骨密度仪(DEXA)与螺旋QCT对骨密度检查之比较[J].医疗设备信息,2000,15(1):54-55.
[33]Prall WC,Haasters F.Mesenchymal stem cells from osteoporotic patients feature impaired signal transduction but sustained osteoinduction in response to BMP-2 stimulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2013;440:617-622.
[34]Peichl P,Griesmacher A,Muller MM,et al.Serum osteocalcin and urinary crosslaps are suitable markers of bone in response to short term hormone replacement therapy. Gynecol Endocrinol.2000;145:374-381.
[35]Takayanagi H,Kim S,Matsuo K,et al.RANKL maintains bone homeostasis through c-Fos dependent induction of interferon-β. Nature.Nature.2002;416:744-774.
[36]Chen GQ,Deng CX,Ping Y.TGF-B and BMP signaling in osteblast differentiation and bone formation.Int J Biol Sci. 2012;8(2):272-288.
[37]罗涛,刘天涛,郭吕华,等.基因活化的仿生生物材料促进骨再生的实验研究[J].医学信息,2014,22(8):110-111
[38]Valverde P,Tu Q,Chen J.BSP and RANKL induce osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption synergistically.J Bone Miner Res.2005;20(9):1669-1679.
[39]Miyamoto T.Regulators of osteoclast differentiation and cell-cell fusion. Keio J Med.2011;60(4):101-105.
[40]Van der plas A,Nijweide PJ.Cell-cell interaction in the osteogenic compartment of bone.Bone.1988;9(2):107-111. |